Workflow automation of oil and gas enterprise

As socially responsible corporation, KPO works towards generating maximum social and economic benefits from the Karachaganak field and so utilizes high-tech software to solve its production tasks.
Discovered in 1979, the Karachaganak field is one of the world’s largest gas and condensate fields located in north-west Kazakhstan near Aksay city. Its area of over 280 square kilometers carries 9 billion barrels of condensate and 48 trillion cubic feet of gas as estimated initial reserve of hydrocarbons.
In 2018, Karachaganak Petroleum Operating B.V. (hereinafter KPO) managed to reach its record production level of 148 million barrels of oil equivalent of stabilized and unstabilized liquid hydrocarbons, crude and fuel gas. At that, 8.6 billion cubic meters of gas, which is approximately 45.4 per cent of the total gas produced, were re-injected to maintain reservoir pressure.

Being a socially responsible corporation, KPO works towards generating maximum social and economic benefits from the Karachaganak field and so utilizes high-tech software to solve its production tasks. Effective monitoring and maintenance of such a huge territory are not possible without automation of field works and comprehensive approach to their management.
Development of subsystem for automation of creation of offline maps used on mobile devices
At the conference in 2017 Moscow, KPO specialists got interested in the exhibited Data East’s software products and soon became corporate users of extension as part of the project called ‘Development of subsystem for automatization of creation of offline maps for mobile devices’.

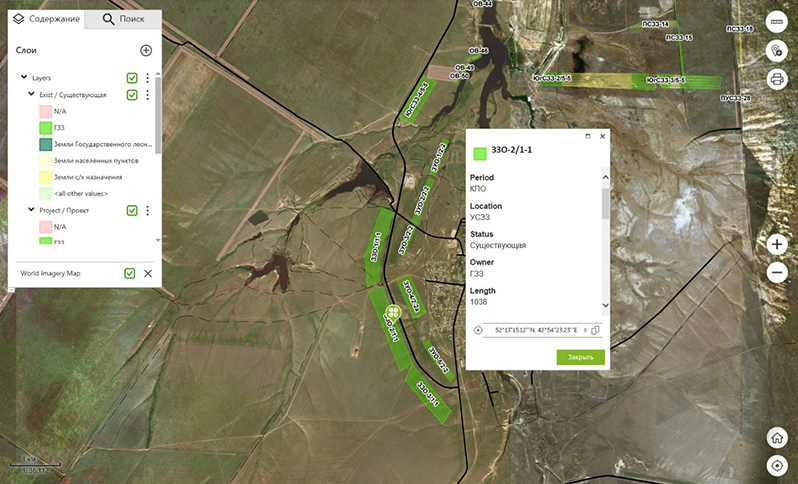
The purpose of this subsystem for automating the creation of offline maps is to check for changes in the administrator’s digital cartographic data since the last map was created, and to start generating new maps in CMF2 format when changes are detected.
These mobile maps are then used by KPO employees on iOS, Android and Windows devices via GIS KPO, a custom-made mobile app developed by Data East for Karachaganak Petroleum Operating B.V. That is, KPO can not only create actual offline maps of Karachaganak field, but also promptly provide its field staff with these maps. Besides, during conversion of the project to mobile map, the customized native legend and all attributes are preserved, which means that symbology accepted at KPO can be used to add new objects when working with mobile map.

Benefits of using mobile maps
With mobile maps, KPO solves various tasks related with field landscaping and planting, wellbores monitoring and maintenance, repair, construction and planned works in the field, etc. Besides, mobile offline maps allow finding your bearings on site, estimate spatial location of objects, perform measurements, define borders of project works, update cartographic data in the field, provided that all these tasks can be solved without internet availability.

Control of quarantine weeds dispersal on field territory
To maintain unhampered access to wellbores, the timely mowing of quarantine weeds should be done, which is a series of measures directed to prevent occurrence and dispersal of hazardous plants on the territory of Karachaganak field.
Before start of field works, the territory is inspected and analyzed, the areas of quarantine weeds growing are defined. Collected data are submitted to geoinformation system of administrator via simple data export. After that the area of plants mowing is calculated and based on this calculation the appropriate order for contracting organization is created. Along with this order, contracting organization is provided with mobile map in CMF2 format showing areas of hazardous plants where mowing needs to be done.
As a rule, such mobile map includes road network, infrastructure objects and industrial facilities of the field. With the mobile app on the device, the ordering party can get geographical bearings on site and monitor scope of performed works. Thus, to control works performance, the KPO’s inspector with mobile app GIS KPO goes to the site. In the offline mode inspector registers all details of made works on the map of the mowing site. Upon return to the office, all data collected by inspector are synchronized with data stored in the geoinformation system of administrator. Based on detected changes the updated map showing areas where mowing works have been completed, is automatically created. The new map is forwarded to contractor and the process is repeated until full completion of mowing works.
Maintenance of forest protective belt on field territory
For maintaining of forest protective belts of Karachaganak field KPO hires contracting organizations that use mobile maps as information guide and as tool to find geographical bearings on site.
All data about location of forest protective belts and scope of their maintenance works are stored in the geoinformation system of administrator. Based on this data the mobile maps in CMF2 format are created. These maps show names and calculated areas of forest protective belts and protective structures, if any. Contractor’s field crew is provided with maintenance order containing scope of works regarding forest belts and mobile map of the appropriate area.
Mobile maps enable automating field works and promptly getting up-to-date information about status of recently performed works without attendance on site in person. This technology allows integrating collected field data to corporate geoinformation system GIS KPO. Using the mobile maps technology for maintenance of the world’s largest Karachaganak gas and condensate field, led to increase of raw products extraction and to decrease of emergency situations during field works.
Such workflow automation and integration of digital cartographic data with mobile solutions provided for analysis and inspection of field works allow quickly and efficiently making decisions in the course of maintenance of Karachaganak field.
Data East team together with Eugene Kotelnikov (KPO B.V.)